Ecosystem as an accelerator of 6G
“We ensure that 6G innovations don't remain stuck in the lab, but are tested, validated, and prepared for the market.”
Program Line 4 within Future Network Services (FNS) focuses on strengthening the Dutch 6G ecosystem: from technology development to application, from start-up to international standard. Lenneke de Voogd (TU Delft Innovation & Impact Centre) explains how PL4 accelerates innovation through collaboration, test facilities, and international positioning.
From technology to applicable innovation
Where other program lines focus more on fundamental technology or specific use cases, Program Line 4 plays a connecting and accelerating role.
"Program Lines 1 and 2, for example, develop 6G chips, AI-driven network software, and new network architectures. Program Line 3 translates that into concrete applications, such as smart mobility, industrial automation, or wireless sensing. We ensure that the innovations come together, are tested in practice, and actually create value.
This is done through instruments such as the National 6G Testbed, regional 6G Fieldlabs, international standardization, startup support, human capital initiatives, and technology-policy co-development.
Where 6G becomes tangible
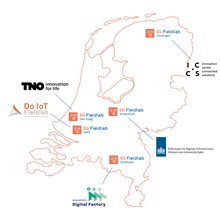
Strengthening the Netherlands' earning capacity is central to PL 4. The National 6G Testbed and the affiliated 6G Fieldlabs in Delft, Groningen, Eindhoven, The Hague, and Amersfoort play a key role in this.
“These are the places where 6G becomes concrete: where new 6G components from parties such as NXP are validated in a realistic network environment, where startups test their AI software modules, and where SMEs experiment with applications such as automated drone inspections.”
By giving researchers and companies access to advanced facilities, expertise, and partners at a pre-commercial stage, FNS reduces risks and accelerates the step to market introduction.
“When 6G is commercially rolled out, these companies will already have tested, learned, and scaled up. That is a huge advantage.”
From test bed to standard and policy
PL 4 does not stop at testing alone. Innovations are actively linked to international standardization and policy. “Through contributions to ETSI and 3GPP, we ensure that Dutch technology actually finds its way into global 6G standards. This is crucial for scalability and for companies' revenue models.”
Technology policy co-development is also an important part of this. A concrete example is the open report on interference scenarios in the Upper 6 GHz band, in which experts analyze technical risks and policy implications for 6G in the Netherlands. “This type of in-depth analysis helps policymakers make well-informed choices in a timely manner and prevents regulations from unintentionally slowing down innovation – a lesson we learned from the 5G rollout.”
Results and milestones
The progress of Program Line 4 in phase 1 is proceeding according to plan.
“An important result is that the National 6G Testbed is now up and running as a single federated infrastructure. Not six separate field labs, but one coherent national testbed.”
In addition, several research projects have been supported through innovation tickets, six of which have since grown into spin-offs. A solid foundation has also been laid for Learning Communities, which are directly linked to the 6G Fieldlabs. This allows MBO, HBO, and WO students to gain practical experience with 6G technology together with companies, which is essential for building up a sufficiently qualified workforce for the upscaling of 6G in the Netherlands.
Collaboration is essential – and sometimes exciting
An important challenge was to break through the fragmentation.
“A lot was already happening in the Netherlands in the field of 5G and Beyond 5G, but often in isolation from each other. We brought these initiatives together, both technically and organizationally. That requires trust, especially when competitors are working together.”
PL4 also helps partners take a closer look at their position in the value chain. “Not just: what are we building? But also: for whom, when, and how does this fit into the bigger picture?”
Highlights
An important moment was the launch of the National 6G Testbed on October 7.
“That was the moment when we could say: this is no longer a plan, this is reality.”
Lenneke also mentions the international visibility of Dutch startups as a highlight, for example at Mobile World Congress and 4YFN in Barcelona.
“There you see entrepreneurs pitching their 6G innovations to international investors and partners. That's where everything comes together.”
Looking ahead
As phase 1 draws to a close, the focus is on concrete experiments in the National 6G Testbed and on further international collaboration, including with Japan, Taiwan, and European 6G initiatives.
In phase 2, support for startups and scale-ups will be further strengthened through a separate program line called: Acceleration & access to finance.
“This offers enormous potential for new business activity and long-term earning capacity for the Netherlands.”
Call to the network
Finally, Lenneke emphasizes the importance of collaboration.
“Ecosystem development is teamwork. It requires openness, clear choices, and a willingness to invest together in something that is bigger than your own organization.”
According to her, this is also where FNS's strength lies: working from value chains and co-creation, so that 6G innovations are not only developed but also have a real impact.